
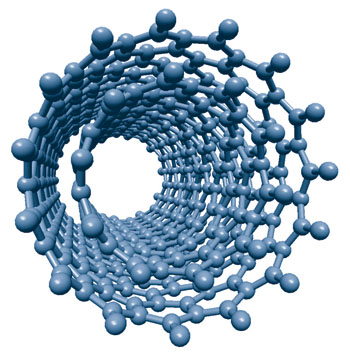
On a molecular level, CNTs are 100 times stronger than steel at one-sixth the weight and have a very large aspect ratio making them very useful as a mechanical property enhancing filler material.Ĭarbon Nanotubes conduct heat and electricity similar to copper but without oxidative concerns provided that they are well dispersed.Ĭarbon Nanotubes have already found commercial applications in the fields of engineering plastics, polymers, displays, anti corrosion paints, thin films and coatings, transparent and non-transparent conductive electrodes, super hydrophobic coatings and anti-static packaging while active research is on going in fields such as batteries, fuel cells, solar cells, advanced devices, optics, water desalination and many others.Ĭarbon Nanotubes paved the way for Graphene.Īllotropes Of Carbon Featuring Diamond, Graphite, and Carbon Nanotubesīeing a tube-like material. Our carbon nanotubes overview is designed to give the reader an in depth understanding of these amazing materials. In fact, a 4th state of matter was recently discovered as water trapped inside a carbon nanotube doesn’t act as a solid, liquid, or gas. These functional nanoscale materials have a variety of unique, fascinating, and never seen before properties. Hundreds of millions of dollars have been invested trying to unlock the secrets of these revolutionary materials. Since the discovery of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) in 1991 by Iijima, a whole new discipline in materials science has developed, Nanoscience. Please also visit our Carbon Nanotubes Properties And Applications Guide Here Carbon Nanotubes History And Production Methods Double Walled Carbon Nanotubes Structure This property means these nanotubes can be used in electronics.Carbon Nanotubes History And Production Methods is intended to convey a general understanding of what Carbon Nanotubes are, their history, synthesis, & purification methods.

Carbon nanotubes and fullerenes free#
Like graphene, carbon nanotubes can conduct electricity because it contains delocalised electrons which are free to move throughout the single sheet of carbon atoms and carry charge.

Graphen e is made up of a single layer of hexagonal rings, with each carbon atom bonded to three other carbon atoms meaning each carbon atom has one delocalised electron (like graphite). Graphene is a single layer of graphite.Graphene & Fullerenes (GCSE Chemistry) What is Graphene?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
